Var Shankar, Executive Director, Responsible AI Institute and Steve Mills, Managing Director & Partner, Chief AI Ethics Officer, Boston Consulting Group (BCG)
AI Governance Mechanisms Overview
AI governance mechanisms range from laws and regulations that apply to AI systems to so-called ‘soft law’ mechanisms. The figure below provides a high level summary of AI governance mechanisms, which are explained in greater detail in A Guide to AI Governance for Business Leaders.
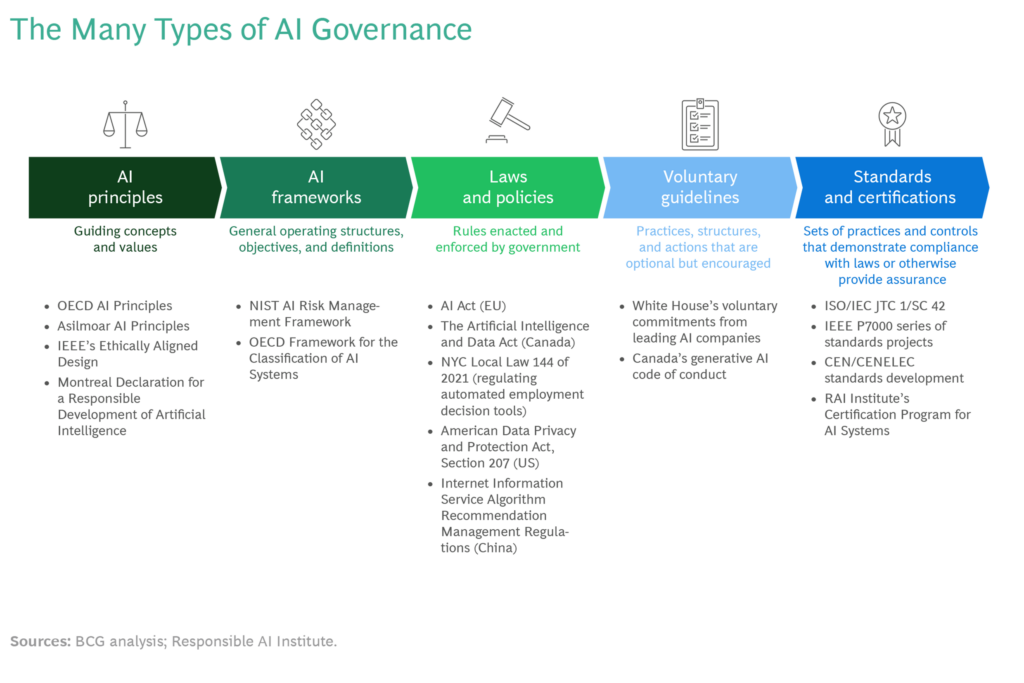
Since AI standards play an important role in the recently-passed EU AI Act, they have attracted renewed interest from business leaders and policymakers.
Why Should Business Leaders use AI Standards?
AI standards provide a common view of ‘what good looks like’ with respect to a framework, law, policy, or guideline. Since AI standards are developed collaboratively by recognized experts in the field, they provide clear and authoritative guidance to business leaders to assure them that AI governance they put in place aligns with global best practices.
Additionally, policymakers and regulators often look to standards as a means to evaluate regulatory compliance, yielding further benefits for companies to comply with these standards. For example, two European Standardization Organizations, the European Committee for Standardisation (CEN) and the European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardisation (CENELEC), will create or adopt harmonized European standards that will clarify the requirements included in the EU’s proposed AI Act, including risk management, data quality and governance, technical documentation, record keeping, transparency and provision of information to users, human oversight, accuracy, robustness, and cybersecurity.
Many experts expect that ISO/IEC 42001, published in December 2023, will be adopted by CEN-CENELEC and therefore become a harmonized European standard. This will allow organizational alignment with the requirements of ISO/IEC 42001 to serve as evidence of an organization’s efforts to comply with the AI Act.
AI standards can provide common objectives, guidelines and specifications for organizations, policymakers, and researchers. AI standards are flexible and multifaceted. A standard can be generally applicable or applicable in limited circumstances and can operate at the organizational or system level. The UK’s AI Standards Hub includes nearly 300 AI-related standards. Perhaps most importantly for businesses, it is certifiable and auditable, allowing organizations to demonstrate compliance to customers, partners, regulators, and other interested parties.
Leading AI Standards from ISO/IEC

ISO/IEC 42001 – This standard provides guidance on establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving a management system for AI. A management system is a way for an organization to achieve its objectives related to a topic. For example, the well-known ISO/IEC 27001 standard on Information Security Management Systems helps organizations adopt a holistic approach to manage existing and emerging information security risks. ISO/IEC 42001 applies to organizations of all sizes and provides requirements and implementation guidance. It addresses organizational objectives, policies, governance, resourcing, leadership, monitoring, and a range of other factors related to AI use. ISO/IEC 42001 is also a certifiable and auditable standard.
The NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF) is sometimes compared to ISO/IEC 42001. While both documents provide organizations with authoritative guidance at the organizational level, ISO/IEC 42001 is a standard that provides implementation guidance and is meant to be audited and certified against, while the AI RMF is a framework that provides foundational concepts and definitions for the responsible AI community to adopt.
ISO/IEC 23894 – This standard provides guidance on AI risk management across an organization and provides detailed guidance on how to design and administer AI product-level risk assessments. Like the widely-adopted and more general ISO 31000, ISO 23894 focuses on risk management. The clearer focus on risk sets ISO/IEC 23894 apart from ISO/IEC 42001. ISO/IEC 23892 covers AI risk assessment and treatment at an organizational level and through each stage of the AI lifecycle. In the interest of clarity, NIST has mapped the functions of its AI RMF to ISO/IEC 23894.
Why should business leaders contribute to AI standards?
By contributing to AI standards development, business leaders can help shape the AI governance landscape with lessons from their organizations and gain early access to emerging best practices and issue areas. Business leaders can contribute to international standardization through national or regional standardization committees or directly with ISO, IEC, IEEE and other global standards organizations. Though standardization has a reputation for being technical and guided by large organizations, standards development organizations are making significant efforts to include social and environmental considerations in AI standards and to involve smaller organizations.
How can business leaders leverage AI standards?
Business leaders can take these steps to get started with AI standards:
1. Determine objectives for using AI standards
Three common purposes are aligning an organization’s AI governance with global best practices for AI, improving and demonstrating regulatory compliance, and shaping the AI governance landscape.
2. Select AI standards
Focus first on well-known AI standards, such as ISO/IEC 42001 and ISO/IEC 23894. These standards will have more robust supporting communities and their terms and concepts may be incorporated by suppliers, customers, end-users and government organizations. In many cases these are also certifiable and auditable.
3. Inventory which standards your organization using and identify areas of expertise
Which functions in your organization are using standards already? These functions can serve as sources of expertise and pilot candidates for introducing new standards. For example, your cybersecurity function may be using the ISO/IEC 27001 standard on information security or your risk function may already be using the ISO/IEC 31000 standard on risk management. These teams will be valuable sources of information on how to best adopt and conform to new standards.
4. Conduct a gap analysis and understand steps to alignment
Map the selected AI standards to your organization’s existing AI strategy, governance, and processes and identify gaps. Determine importance and estimated cost for each gap. Prioritize gaps to address based on your organization’s objectives. Create a roadmap to help the organization move from current state to compliant and auditable.
5. Engage in standards processes
Contribute to the development of AI standards through national committees or directly with standards organizations to share lessons from your organization, shape the AI governance landscape and stay on top of emerging best practices.
ABOUT BOSTON CONSULTING GROUP
Boston Consulting Group partners with leaders in business and society to tackle their most important challenges and capture their greatest opportunities. BCG was the pioneer in business strategy when it was founded in 1963. Today, we work closely with clients to embrace a transformational approach aimed at benefiting all stakeholders—empowering organizations to grow, build sustainable competitive advantage, and drive positive societal impact.
Our diverse, global teams bring deep industry and functional expertise and a range of perspectives that question the status quo and spark change. BCG delivers solutions through leading-edge management consulting, technology and design, and corporate and digital ventures. We work in a uniquely collaborative model across the firm and throughout all levels of the client organization, fueled by the goal of helping our clients thrive and enabling them to make the world a better place.
About Responsible AI Institute (RAI Institute)
Founded in 2016, Responsible AI Institute (RAI Institute) is a global and member-driven non-profit dedicated to enabling successful responsible AI efforts in organizations. We accelerate and simplify responsible AI adoption by providing our members with AI conformity assessments, benchmarks and certifications that are closely aligned with global standards and emerging regulations.
Media Contact
Nicole McCaffrey
Head of Marketing, RAI Institute
+1 (440) 785-3588
Follow RAI Institute on Social Media
X (formerly Twitter)





