Recruiters and Hiring Managers increasingly use Artificial Intelligence tools to find new employees. Different platforms offer AI solutions at various stages of the hiring process. Many of them claim to make the hiring process more effective, cost- and time-efficient, and at the same timeless biased than traditional hiring methods. Critics see the risk that AI and Algorithms can exacerbate existing biases and introduce new ones.
Use of AI tools throughout the hiring process
To understand the challenges and risks involved, it helps to divide the hiring process in different stages, at which different AI tools are used. It can roughly be split up in three sections: sourcing, screening, and selection. The different categories overlap somewhat, as sourcing can contain screenings/assessments to filter out unsuitable candidates, and the selection phase continues to assess to see whether the chosen candidate should actually be employed.
To separate the different phases, we define sourcing for any job-related activities before the actual application. The screening/assessment phase happens after the candidates have actually applied and before they are selected. In the selection phase, the candidate is taken out of the candidate pool and any further assessment is only used after they are already chosen.
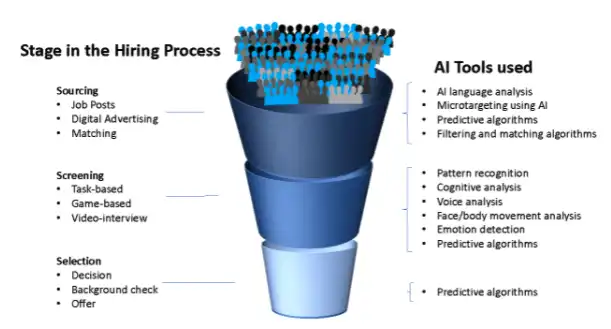
Graphic inspired by the Hiring Funnel used in Miranda Bogen and Aaron Rieke, 2018, HELP WANTED. An Examination of Hiring Algorithms, Equity and Bias (2018)
Sourcing
During the sourcing phase recruiters try to find and target the right candidates. It is especially useful in jobs where it is hard to find job seekers with the necessary qualifications and the demand is higher than the supply of potential candidates.
Sourcing with the help of AI includes writing a job post, digital advertising, and matching systems. Specialized AI tools help with each of these tasks. AI using language analysis can detect which kind of language appeals to what audience in a job post, microtargeting such as behavioral targeting can be used to place the job ad at strategic places like specific social media, or specialized job aggregate websites. Filtering and matching algorithms can sort through large masses of data and explore multiple different resources to bring together the right groups of candidates with the right employer. Predictive algorithm and machine learning are part of the sourcing process to figure out the desired candidates.
Screening
The screening or assessment phase mostly serves to narrow down a pool of candidates after assessing their job-related qualifications. It is especially useful in scenarios where there is a large candidate pool and human recruiters do not have enough time to go through all of the applications.
Such assessments can be done in different ways. There are three main categories; task-related assessments, game-related assessments and video interviews. Task-related assessments often have skill-specific questionnaires or test specific skills, such as math tests or coding challenges. Game-related assessments gamify the testing and are often designed to assess the cognitive abilities of candidates. Video interviews can use facial analyses, speech analyses or other biometric analyses like body movements analysis to detect personality traits or emotions in addition to using natural language processing to analyze the content of the interview. During screening, various advanced AI tools, machine learning, and predictive algorithms such as recommender systems are used.
Selection
In the selection phase, the decision is made. However, predictive AI tools can still be used. They can determine what kind of offer, including the salary, would most likely be accepted by the chosen candidate. Or, after conducting a thorough background check via AI tools, it could be determined how likely the candidate would be to stay in the company or be a potential risk (like a potential sexual harasser). This process also includes predictive algorithms and machine learning.
Other AI uses
In addition to the ways AI is used in hiring described above, many companies use conversational AI such as chatbots to answer frequently asked questions, schedule appointments, and do basic screening. These tools are used throughout the process, on company websites, once the application process has started with concrete candidates or as a scheduling tool for scheduling tests or interviews or getting through administrative questions for the final offer. They use natural language processing, and to some extent predictive algorithms.
Risks of using AI hiring tools
Issues that can arise with all of these AI hiring tools include, among others, inaccurate decisions and exacerbation of biases. Biases can enter at various stages. They can be historic, systemic or there can be automation bias. The training data used can already be biased, the premises like a culture fit requirement for an already gender and/or race-biased company can accelerate the bias, and hiring managers can have automation bias. At the same time, AI tools can also be used to mitigate bias and provide a more level playing field.
To make sure that this high-impact sector uses AI tools in a responsible way, puts safeguards into the right places and mitigates rather than exacerbates biases, an awareness of potential risks, transparent AI systems and independent audits are crucial. To design adequate assessments for such audits, the impact and potential harms these tools have on different parts of society need to be identified and taken into account. Appropriate feedback of all relevant stakeholders is essential for this process.
RAII is developing a certification in the Employment Context that assesses ethical dimensions including bias, transparency and accountability, and seeks input from various disciplines and areas like HR, Law, Tech or Policy.
The first meeting of its Employment Working Group will be on February 14th, 2022 at 2:00 EST. Please sign up here to attend.




